ASP.NET Core Web API: Troubleshooting
This document will help you troubleshoot your configuration if you get 401 (Unauthorized) response from your API.We recommend that you log in to follow this quickstart with examples configured for your account.
If the configuration of your JSON Web Token (JWT) middleware does not match the JWT that was passed to the API, you get a 401 (Unauthorized) response from your API.
This document will help you troubleshoot your JWT middleware configuration.
Check the Token Validation
There are 5 criteria for validating a JWT token.
-
Is the token formed properly? Check if the structure of the token matches the structure of a JSON Web Token. Read more about the JSON Web Token structure.
-
Has the token been tampered with? The last part of a JWT is the signature. The signature is used to verify that the token was signed by the sender and not altered in any way.
-
Has the token been received in its validity period? JWTs are only valid for a specified time, defined in the
expclaim. -
Is the token coming from the intended Authority? Check the following two criteria:
-
Signature verification: Check if the JWT is correctly signed with the key issued by the issuing authority.
-
Issuer value: The Issuer is defined in the
issclaim. Check if this claim matches up with what your application expects.
-
-
Is the token intended for the current application? Check if the
audclaim of the JWT matches with what your application expects.
Inspect a Token
You can inspect a JWT with the JWT.io website. Use the debugger on the website to check if your JWT is well formed. You can also inspect values of the various claims.
The screenshot below shows the following information:
- The token is signed with the RS256 algorithm
- The issuer of the token is
https://jerrie.auth0.com/ - The audience of the token is
https://rs256.test.api
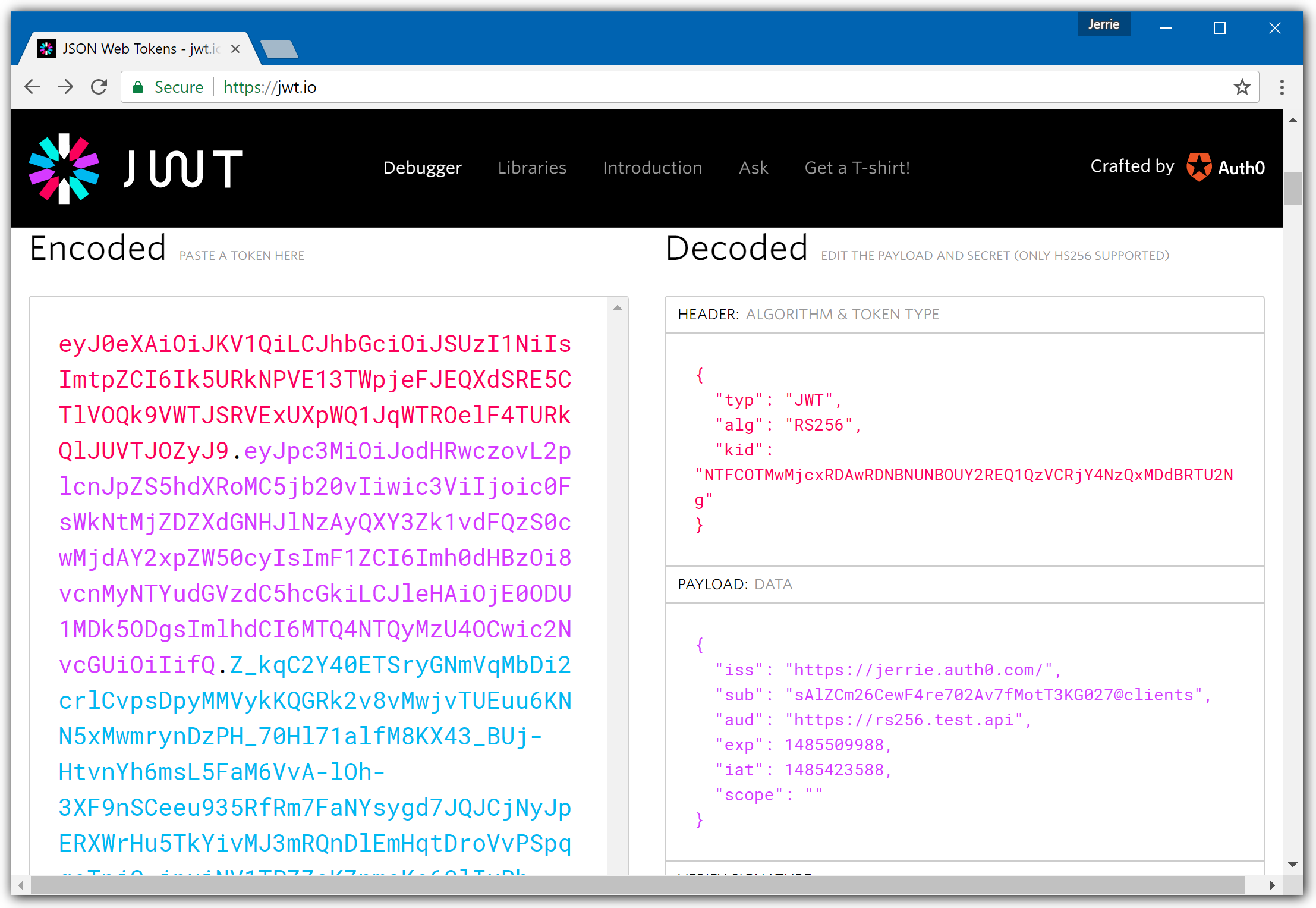
Check if the values of the JWT token match exactly the values in your JWT middleware registration. This includes the trailing slash for the Issuer.
var options = new JwtBearerOptions
{
Audience = "https://rs256.test.api",
Authority = "https://jerrie.auth0.com/"
};
app.UseJwtBearerAuthentication(options);Was this helpful?
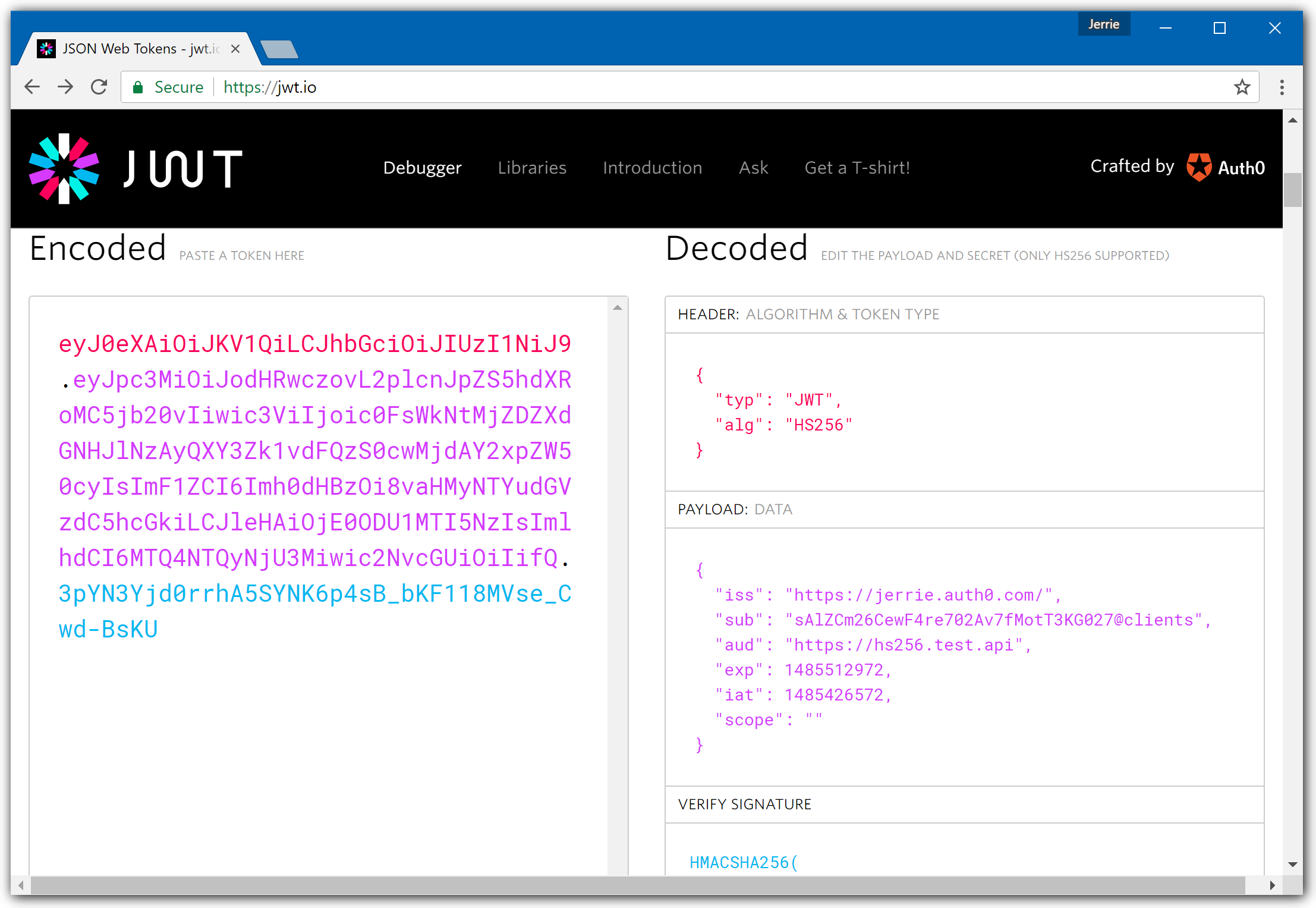
If your token is signed with the HS256 algorithm, the debugger view is different.
The screenshot below shows the following information:
- The token is signed with the HS256 algorithm
- The issuer of the token is
https://jerrie.auth0.com/ - The audience of the token is
https://hs256.test.api
If your token is signed with the HS256 algorithm, the middleware needs to be configured in the following way:
var options = new JwtBearerOptions
{
TokenValidationParameters =
{
ValidIssuer = "https://jerrie.auth0.com/",
ValidAudience = "https://hs256.test.api",
IssuerSigningKey = new SymmetricSecurityKey(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("your api secret"))
}
};
app.UseJwtBearerAuthentication(options);Was this helpful?
Debug Configuration Issues Using Log Files
To debug potential configuration issues, inspect the log files for your application. For more information, refer to the Logging in ASP.NET Core document.
In this example, we run the application from the command line and inspect the console log output.
1. Are you passing the JWT in the Authorization header?
Check if you are passing the JWT as a Bearer token in the Authorization header of the HTTP request.
If you are not passing the token, you will see the following warning:
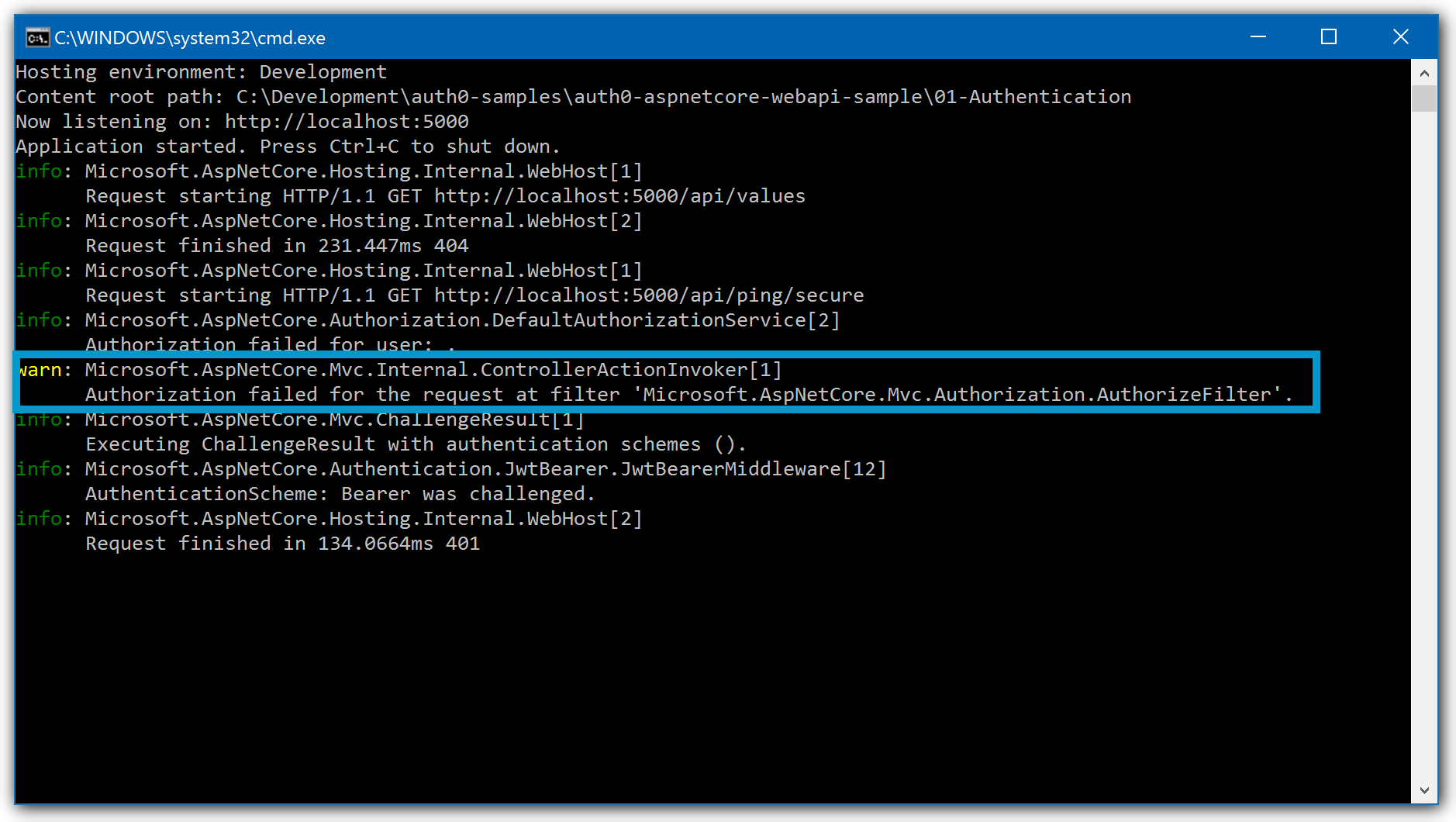
Look for the following warning message:
Authorization failed for the request at filter 'Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Authorization.AuthorizeFilter'Was this helpful?
To resolve this issue, make sure you are passing the JWT as the Bearer token in the Authorization header of the HTTP request.
2. Did you configure the JWT middleware for the correct signing algorithm?
Make sure that the signing algorithm you used to sign your token matches the signing algorithm configured in your middleware.
The following screenshots show two messages:
- A warning message: "Authorization failed..."
- A message with more information
The following example shows that the JWT is signed with the HS256 algorithm and the middleware is configured to expect RS256 tokens:
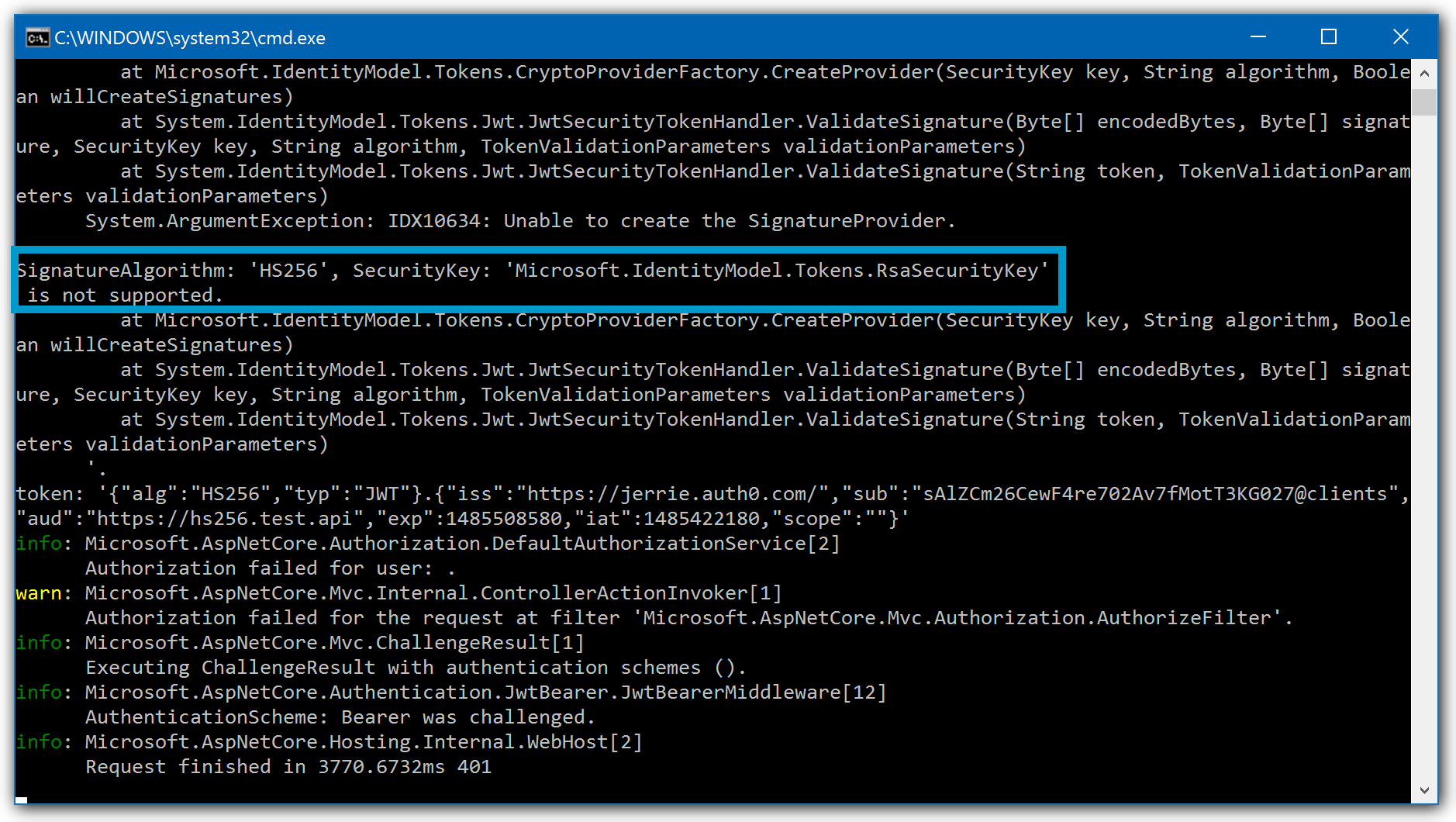
Look for the following warning message:
System.ArgumentException: IDX10634: Unable to create the SignatureProvider.
SignatureAlgorithm: 'HS256', SecurityKey: 'Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens.RsaSecurityKey' is not supported.Was this helpful?
The following example shows that the JWT is signed with the RS256 algorithm and the middleware is configured to expect HS256 tokens:
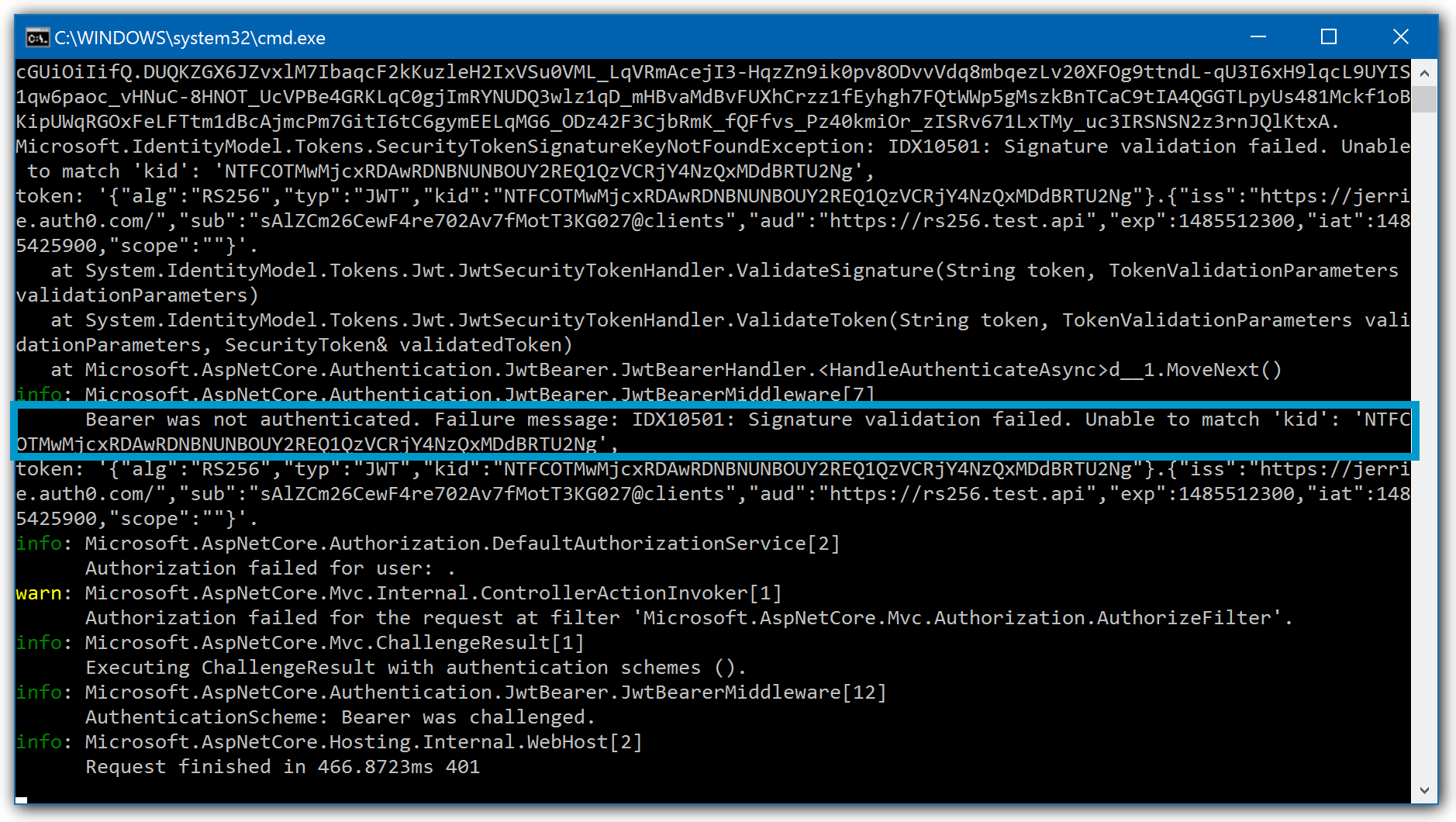
Look for the following warning message:
Bearer was not authenticated. Failure message: IDX10501: Signature validation failed. Unable to match 'kid': 'NTF...'Was this helpful?
To resolve this issue, make sure that the algorithm for the JWT matches with the configuration of your middleware.
3. Has your token expired?
Each JSON Web Token is valid until the time defined in the exp claim runs out. If you send an expired token, the token will be rejected:
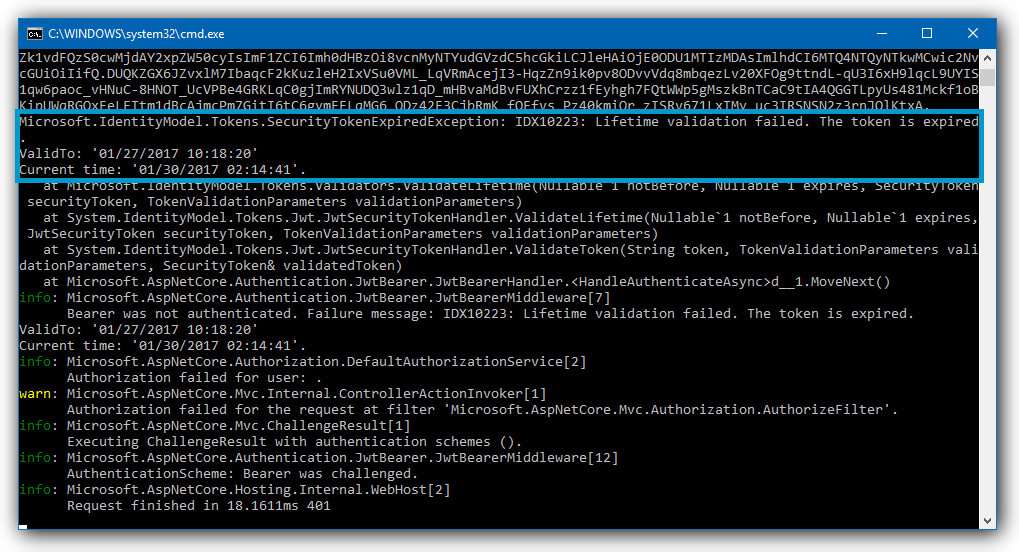
Look for the following error message:
IDX10223: Lifetime validation failed. The token is expiredWas this helpful?
To resolve this issue, check if the token you are sending has not expired.
4. Did you configure the correct issuer?
The Issuer specified in your token must match exactly with your JWT middleware configuration.
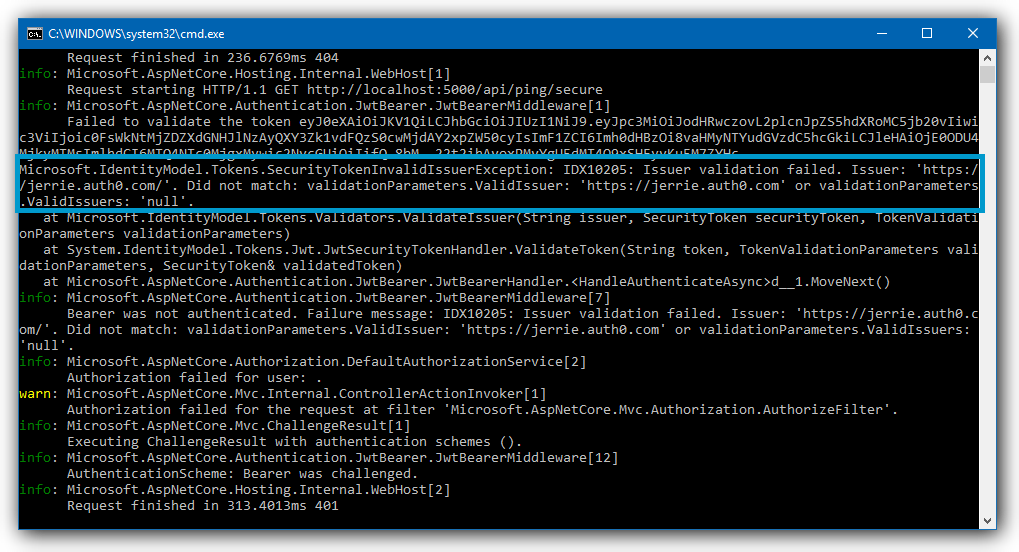
Look for the following warning message:
IDX10205: Issuer validation failed.Was this helpful?
To resolve this issue, make sure that you specify the correct issuer for your JWT middleware.
For HS256 signed tokens, specify the correct value for the ValidIssuer property of TokenValidationParameters.
5. Does the audience match your JWT middleware configuration?
Check if the audience specified in your token matches your JWT middleware configuration.
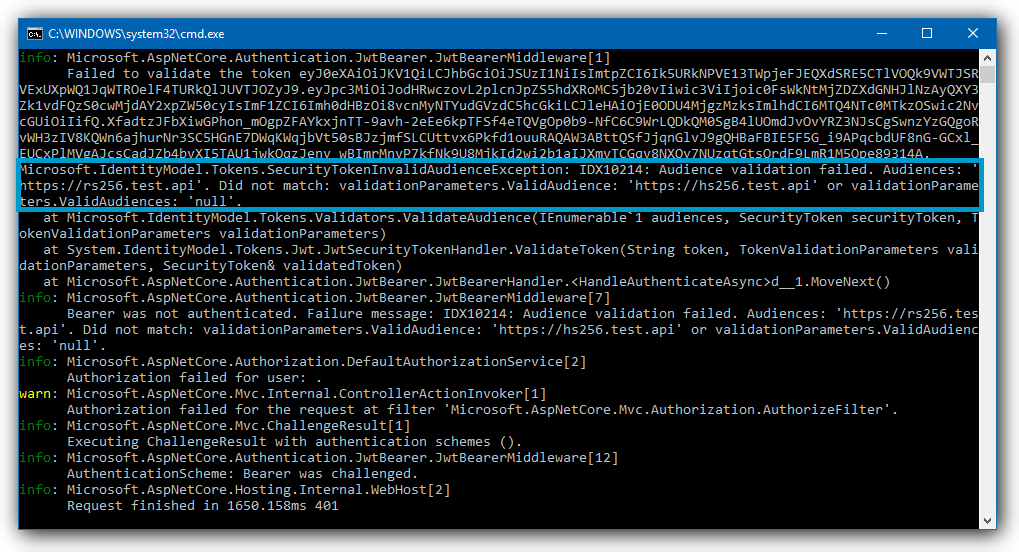
Look for the following error message:
IDX10214: Audience validation failedWas this helpful?
To resolve this issue, make sure you specify the correct audience for your JWT middleware. Depending on how your JWT middleware was configured, do the following:
- Set the correct
Audienceproperty ofJwtBearerOptions - Set the
ValidAudienceproperty ofTokenValidationParameters