Rotate Signing Keys
You can manually rotate a signing key periodically to change the JSON web key (JWK) key used by applications and APIs to validate tokens. If your application or API does not allow for this key change, and it attempts to use an expired signing key to verify a token, the authentication request will fail.
Although Auth0 signs with only one signing key at a time, your tenant's OpenID Connect (OIDC) discovery document always contains multiple keys. The OIDC discovery document will always include both the current key and the next key, and it may also include the previous key if the previous key has not yet been revoked. To provide a seamless experience in case of an emergency, your application should be able to use any of the keys specified in the document. To learn more about OpenID Connect discovery documents, read Locate JSON Web Key Sets.
You can rotate your tenant's application signing key using the Auth0 Dashboard or the Auth0 Management API.
Use the Dashboard
Go to Dashboard > Settings > Signing Keys.
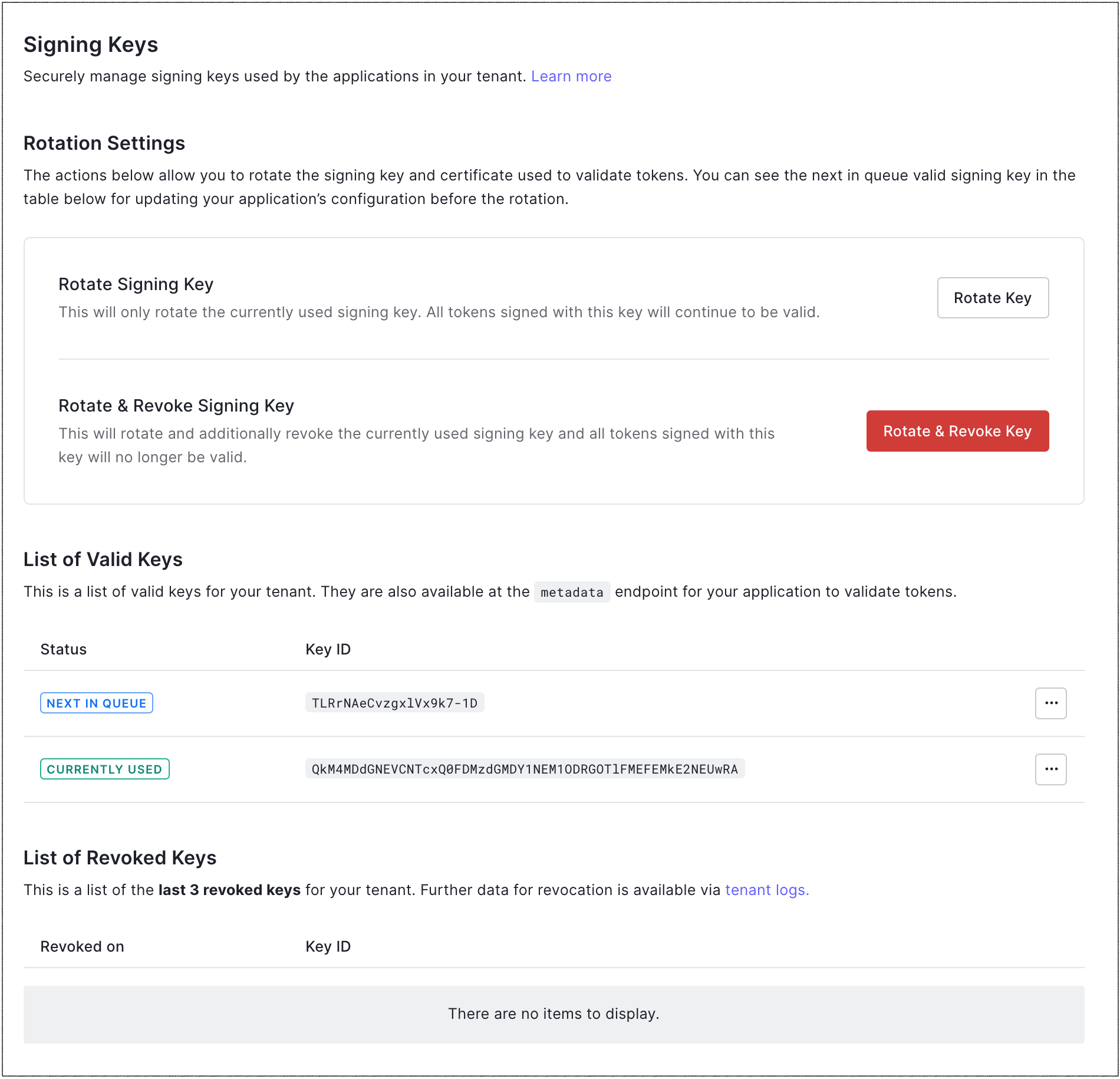
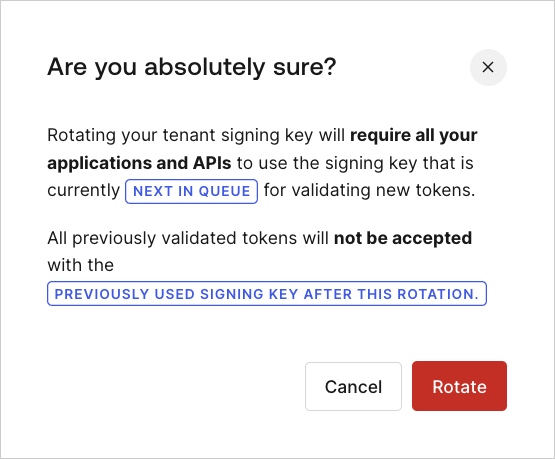
Under Rotation Settings, locate Rotate Signing Key, and select Rotate Key.
Click Rotate to confirm.
Use the Management API
To get a list of the signing keys, make a
GETcall to the Get all Application Signing Keys endpoint.To rotate the signing key, make a
POSTcall to the Rotate the Application Signing Key endpoint. Be sure to replace theMGMT_API_ACCESS_TOKENplaceholder value with your Management API access token.curl --request POST \ --url 'https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate' \ --header 'authorization: Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}'Was this helpful?
/var client = new RestClient("https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate"); var request = new RestRequest(Method.POST); request.AddHeader("authorization", "Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}"); IRestResponse response = client.Execute(request);Was this helpful?
/package main import ( "fmt" "net/http" "io/ioutil" ) func main() { url := "https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate" req, _ := http.NewRequest("POST", url, nil) req.Header.Add("authorization", "Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}") res, _ := http.DefaultClient.Do(req) defer res.Body.Close() body, _ := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body) fmt.Println(res) fmt.Println(string(body)) }Was this helpful?
/HttpResponse<String> response = Unirest.post("https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate") .header("authorization", "Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}") .asString();Was this helpful?
/var axios = require("axios").default; var options = { method: 'POST', url: 'https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate', headers: {authorization: 'Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}'} }; axios.request(options).then(function (response) { console.log(response.data); }).catch(function (error) { console.error(error); });Was this helpful?
/#import <Foundation/Foundation.h> NSDictionary *headers = @{ @"authorization": @"Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}" }; NSMutableURLRequest *request = [NSMutableURLRequest requestWithURL:[NSURL URLWithString:@"https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate"] cachePolicy:NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy timeoutInterval:10.0]; [request setHTTPMethod:@"POST"]; [request setAllHTTPHeaderFields:headers]; NSURLSession *session = [NSURLSession sharedSession]; NSURLSessionDataTask *dataTask = [session dataTaskWithRequest:request completionHandler:^(NSData *data, NSURLResponse *response, NSError *error) { if (error) { NSLog(@"%@", error); } else { NSHTTPURLResponse *httpResponse = (NSHTTPURLResponse *) response; NSLog(@"%@", httpResponse); } }]; [dataTask resume];Was this helpful?
/$curl = curl_init(); curl_setopt_array($curl, [ CURLOPT_URL => "https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate", CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER => true, CURLOPT_ENCODING => "", CURLOPT_MAXREDIRS => 10, CURLOPT_TIMEOUT => 30, CURLOPT_HTTP_VERSION => CURL_HTTP_VERSION_1_1, CURLOPT_CUSTOMREQUEST => "POST", CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER => [ "authorization: Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}" ], ]); $response = curl_exec($curl); $err = curl_error($curl); curl_close($curl); if ($err) { echo "cURL Error #:" . $err; } else { echo $response; }Was this helpful?
/import http.client conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection("") headers = { 'authorization': "Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}" } conn.request("POST", "/{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate", headers=headers) res = conn.getresponse() data = res.read() print(data.decode("utf-8"))Was this helpful?
/require 'uri' require 'net/http' require 'openssl' url = URI("https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate") http = Net::HTTP.new(url.host, url.port) http.use_ssl = true http.verify_mode = OpenSSL::SSL::VERIFY_NONE request = Net::HTTP::Post.new(url) request["authorization"] = 'Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}' response = http.request(request) puts response.read_bodyWas this helpful?
/import Foundation let headers = ["authorization": "Bearer {yourMgmtApiAccessToken}"] let request = NSMutableURLRequest(url: NSURL(string: "https://{yourDomain}/api/v2/keys/signing/rotate")! as URL, cachePolicy: .useProtocolCachePolicy, timeoutInterval: 10.0) request.httpMethod = "POST" request.allHTTPHeaderFields = headers let session = URLSession.shared let dataTask = session.dataTask(with: request as URLRequest, completionHandler: { (data, response, error) -> Void in if (error != nil) { print(error) } else { let httpResponse = response as? HTTPURLResponse print(httpResponse) } }) dataTask.resume()Was this helpful?
/Value Description MGMT_API_ACCESS_TOKENAccess Token for the Management API with the scopes create:signing_keysandupdate:signing_keys.
Key rotation impact
APIs and API gateways accepting access tokens
Most middleware and API gateways leverage the JSON web key set (JWKS) endpoint to retrieve the current and future signing keys at a certain interval. If your middleware and/or API gateways do not support this endpoint and require you to manually configure a *.cer file, you will need to coordinate the signing key rotation in Auth0 with the reconfiguration of your middleware and gateways.
Regular web applications
When rotating the signing key in Auth0, you will need to coordinate the reconfiguration of your applications which leverage WS-Fed or SAML. This typically happens when you upload the new public certificate or reconfigure the application by entering the WS-Fed/SAML metadata URL. This will change the JWKS key, which is used by applications to validate tokens, make sure your implementation does not assume JWKS keys don’t change.

