Customer Identity and Access Management (CIAM) is how companies give their end users access to their digital properties as well as how they govern, collect, analyze, and securely store data for those users.
CIAM sits at the intersection of security, customer experience, and analytics. Providing an easy, frictionless way for users to onboard and log in is critical for driving conversions and building customer loyalty. Protecting sensitive data from malicious intrusion and taking steps to prevent data breaches is central to a sound security policy and compliance with data privacy laws. And compiling user data into a single source of truth is essential to understanding your customers.
Given CIAM’s complexity and dynamism, many organizations choose to engage a third-party Identity-as-a-Service (IDaaS) provider rather than build a solution in-house.
Below, we’ll discuss the elements of a modern CIAM solution and how your company’s approach to customer identity can impact top-line revenue as well as mediate bottom-line security risk.
Essential Elements of CIAM
Organizations need Identity and Access Management (IAM) solutions for several classes of end-users: employees, enterprise customers, and customers. But each type of user requires a different balance of security and user experience (UX). That’s why CIAM solutions provide a unique set of features distinct from B2B or workforce identity solutions.
Here are four features that form the bedrock of modern CIAM solutions. No two CIAM solutions offer exactly the features in the same way, but if you’re purchasing a CIAM platform, it should include the following:
Scalability
Unlike workforce identity solutions that support thousands of employees and vendors who require fairly static access to a pre-assigned list of applications, CIAM has to scale to millions of users — often in response to short-term events like peak holiday seasons or major sporting events.
Although not traditionally described as a software “feature,” scalability is a unique element of CIAM that requires third-party, cloud-scale stability.
Single sign-on
Single Sign-On (SSO) allows users to log in to one application and automatically be logged into a set of other applications. The most widely known SSO example is Google G Suite, where logging into your Gmail means you’re automatically logged into YouTube, Google Drive, and other Google platforms.
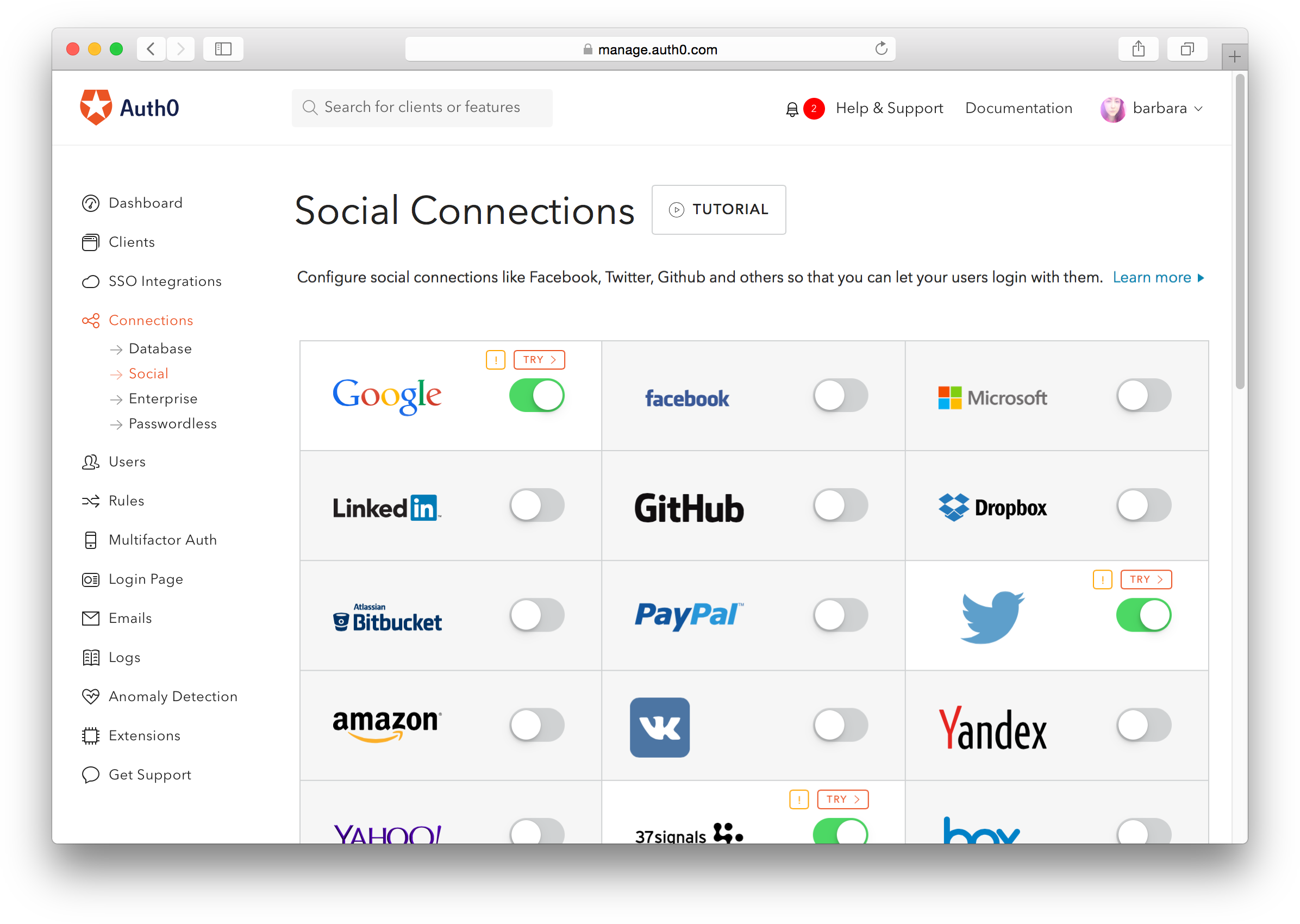
SSO is a basic element of federated identity, and there are SSO options for B2B and workforce IAM solutions. The type of SSO that’s specifically designed for end-users is social login, which allows users to verify their identity with their credentials from a separate provider, like Facebook, Google, or Apple.
Social logins greatly simplify the registration process for users, which can lead to increased conversions and fewer customers abandoning their shopping carts because they got tired of filling out a form. (More on the advantages of SSO later.)
Multi-factor authentication
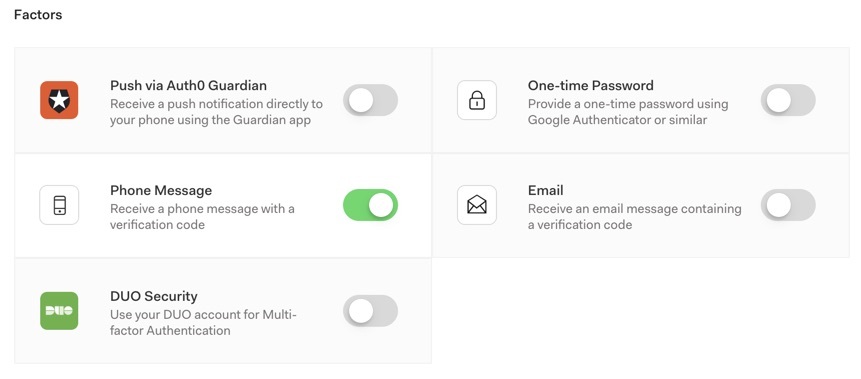
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a more secure means of authenticating user identity than the traditional username/password combination. Passwords are distressingly easy for hackers to steal or guess, so MFA demands an extra credential for users to prove their identity. This could take the form of a one-time PIN sent to the user’s mobile device, an email, or a biometric credential like a fingerprint or face recognition. Auth0 is even releasing a feature in which users can receive a phone call with a voice message of their one-time PIN.
MFA is increasingly regarded as a basic requirement for security, and data privacy laws are beginning to explicitly demand it. However, it’s critical to implement MFA for end-users in a way that doesn’t introduce unnecessary friction. MFA should only be triggered based on the assessed risk, such as when a customer signs in with a new device or makes a suspicious transaction. That’s another reason why it’s critical to have the deep insight into your customers that CIAM provides. So you can assess in context when a transaction requires a higher level of authentication.
Centralized user management
Your insights into your users can be a major competitive advantage, but only if your data is organized, accessible, and accurate. A CIAM solution helps achieve the goal of centralized, data-rich customer profiles that function as a single source of truth about users. That’s because a CIAM solution is essentially an API that mediates between different applications and components, compiling heterogeneous data in one place.
Centralized user management eliminates data silos and duplicate data. Everything you know about a user is together in one place from which admins can quickly grant and revoke permissions. This single view of customers is an obvious advantage for analytics, but it also helps companies meet the reporting requirements of data privacy laws because all profile data is accessible and portable. Knowledge about the user is also critical for building more personalized experiences, which drives higher retention rates.
How CIAM Impacts Business
Now that we’ve gone over the fundamental elements of CIAM, let’s talk about how those elements impact your company’s day-to-day operations and your all-important bottom line.
CIAM Is Central to Data Security
Customer data can be your company’s greatest asset — unless it falls into the wrong hands. A robust CIAM solution has security features to protect against fraud, hacks, and misused data on multiple fronts.
In recent years, the login box has become the front line for fending off intruders. Hackers use broken authentication attacks to steal or guess user credentials and impersonate legitimate users at the login box. One of the most damaging forms of broken authentication attacks is credential stuffing, in which hackers use passwords stolen in one breach to break into other sites. This method works given people’s tendencies to reuse passwords. There are currently billions of stolen passwords being passed around the dark web. Credential stuffing attacks alone cost businesses an average of $4 million a year, according to a 2019 study from the Ponemon Institute.
The best defense against credential stuffing and other authentication-based attacks is a CIAM solution with MFA and brute force protection. Brute force protection stops hackers from flooding your application with login attempts and crashing your site. Meanwhile, MFA ensures that a stolen credential won’t give hackers automatic access to your users’ accounts.
It’s important to note that the amount of damage hackers can do with customer credentials is limited, since they don’t have access to back-end systems. But these attacks can still damage your customer relationships and lead to negative headlines, as in the case of the Disney+ attack.
CIAM systems also help protect your customer data from back-end mischief in the event of a data breach or hack. CIAM solutions govern how you encrypt and anonymize personal data, so it’s useless to data thieves. It’s essential to choose a CIAM system that uses the latest encryption protocols, however, or your databases of sensitive data might as well be written in plain text. Finally, CIAM systems track who within your organization is accessing customer data and alerts admins to suspicious activity. That way, neither an employee nor a bad actor can walk away with your most valuable and sensitive asset: your customer data.
How it affects your bottom line? Cost of data breaches. A 2019 Ponemon study found that the average data breach costs businesses $3.92 million. Businesses who don’t want to budget for that should budget for a modern CIAM solution instead.
CIAM Helps Manage Data Privacy Law Compliance
A new crop of data privacy laws like GDPR and CCPA is fundamentally rewriting the rules for how organizations collect, store, and share personal data (PD). Meeting these legal obligations means managing your approach to CIAM.
To begin with, centralized user management is essential in fulfilling the reporting and erasure requirements of data privacy laws. Under GDPR and CCPA, organizations must provide users, upon request, with copies of their data along with a record of how that data is being used.
Then there’s the issue of MFA. GDPR, CCPA, and New York’s SHIELD Act fall short of explicitly demanding MFA. Still, they require “reasonable” or “appropriate” security measures, and both legal and security experts agree that this means MFA. GDPR enforcement has supported this idea: multiple organizations have been slapped with fines for failing to implement MFA.
Data privacy laws are all about controlling who can access PD, so encrypting customer data and controlling access to it are baseline requirements. A CIAM solution needs to provide all of these elements, as well as tailoring data collection and consent management practices to the relevant laws.
How it affects your bottom line? Cost of regulatory fines. As of May 2020, EU states had issued over €153 million in fines to large and small organizations for non-compliance with GDPR. In November, Californians will vote on the California Privacy Rights and Enforcement Act (CPREA), the so-called “CCPA 2.0.” As the name suggests, the new version will feature a greater emphasis on enforcement. With new laws being passed all the time, the cost of non-compliance can add up quickly.
CIAM Is a Business Enabler Through Customer Experience
A good CIAM solution is the difference between showing up at a crowded restaurant and being told there’s a 20-minute wait and being escorted straight to your table while the bartender mixes your favorite drink. With the right approach to CIAM, you can give your customers easy login and offer them services based on a nuanced understanding of their needs.
Businesses live and die by their conversion rates, and it’s tough out there. In 2019, the average global website conversion rate was 2.58%, which is actually down from 3.42% in 2014. Clearly, today’s customers have no patience for filling out frustrating registration forms. If you use social login, your users get a friction-free registration experience without having to remember another password.
Meanwhile, your company gets the benefit of shared knowledge with that social media provider, so you automatically know your customer’s location, timezone, language, and other details to guide upsell recommendations.
How it affects your top line? Higher conversions and retention, less frustration. Studies have shown that reducing the number of form fields increases conversion rates. With social logins, you can eliminate the form altogether and enable one-click signup. Plus, when users don’t have their own unique password for your business, you save help desk time. Gartner research says between half and a quarter of help desk calls are for password resets. A North American healthcare organization told us it spends approximately $160 to $170 per employee per year on password-related issues alone.
CIAM: A Holistic Approach to Customer Identity Management
As we’ve shown, CIAM plays an increasingly central role in how companies create their digital identities and manage their customer relationships. Given that, companies are allocating more resources to their access management solutions, either from day one or as part of a larger digital transformation.
To learn more about how CIAM can help provide enhanced data protection and seamless customer experience, reach out to the team at Auth0.
About Auth0
Auth0 by Okta takes a modern approach to customer identity and enables organizations to provide secure access to any application, for any user. Auth0 is a highly customizable platform that is as simple as development teams want, and as flexible as they need. Safeguarding billions of login transactions each month, Auth0 delivers convenience, privacy, and security so customers can focus on innovation. For more information, visit https://auth0.com.
About the author

Diego Poza
Sr Manager, Developer Advocacy (Auth0 Alumni)